
Floral Morphology

Floral Morphology
This exercise deals with characters of the flower parts of
a plant. Most items have a visual link, but some do not.
FLOWER COROLLA TYPES
Salverform
- has a slender tube and an abruptly expanded flat limb extending at right
angles to the tube
Bilabiate
- two-lipped flower
Funnelform
- the corolla tube gradually widens; as in morning glory flowers
Campanulate
- bell shaped flower
TERMS FOR FUSION OR JOINING OF FLORAL APPENDAGES
Connate
- fusion of appendages from a single whorl
Adnate
- fusion of appendages from more than one whorl
FLOWER INFLORESENCE TYPES
Corymb
- an inflorescence appearing to have a flat top; indeterminate inflorescence
with outer flowers opening first
Cyme
- more or less flat topped, determinate inflorescence with outer flowers opening
last; a central flower opens first and later flowers are borne on branches below
it. Some cymes are one-sided. Some are scorpioid
cymes, i.e. curled like a scorpion's tail.
Composite
Head - a dense cluster of ray and disk flowers on a very short axis
Umbel
- indeterminate inflorescence ,usually but not necessarily flat topped, with the
pedicles and peduncles arising from a common point; resembles the stays of an
umbrella
Compound
umbel--peduncles arise from one point and each in turn bears a smaller
umbel. Common in the carrot family (Apiaceae)
Spike
- unbranched, elongated, simple, indeterminate inflorescence with sessile
flowers
Spathe
and Spadix - a thick, fleshy flower spike (spadix) surrounded by a leaf or
bract (spathe); ex: closet plant
Solitary
- borne singly or alone
Panicle
- indeterminate, branching inflorescence; the individual branches are either
raceme or corymb-like
Raceme
- simple, indeterminate inflorescence with pedicelled flowers
Verticil
or Whorl--the flowers are borne in a tight circle at each node
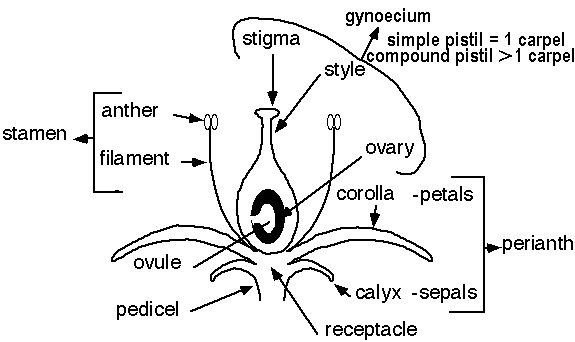
FLOWER PARTS
Female
Pistil
- female part of the flower, composed of a stigma, style, and ovary
Stigma
- the part of the pistil that receives the pollen, located at the tip of the
pistil and often hairy or sticky
Style
- elongated part of the pistil between the stigma and ovary
Ovary
- the part of the pistil that contains the ovules
Male
Stamen
- the pollen bearing organs of a flower, composed of a filaments and anthers
Anther
- the pollen bearing part of the stamen
Filament
- the part of the stamen that supports the anther
Perianth
- the floral envelope, composed of the corolla and calyx
Corolla
- the inner circle of the perianth; collective name for petals
Petal
- an individual part of the corolla used when referring to polypetalous corollas
Calyx
- the outer circle of the perianth; collective name for sepals; usually green
Sepal
- an individual part of the calyx
Pedicel
- attaches flower to stem
FLOWER CATEGORIES DETERMINED BY PARTS PRESENT
Perfect - a flower that contains both pistillate (female)
and staminate (male) parts; may or may not have petals or sepals
Complete - has all four parts of the flower present: sepals,
petals, pistil, and stamen
Staminate - having stamens and no pistils; a male flower
Pistilate - having pistils and no stamens; a female flower
Monoecious - applied to taxa (not flowers) that feature production of both staminate and pistillate flowers on individual plants. The flowers are imperfect but, in terms of sexual function, the individual plant is bisexual. Corn (Zea mays) and Cucumber (Cucumis sativus) both possess staminate/pistillate flowers.
Dioecious - applied - again
to taxa - that comprise populations of plants that produce only staminate or
pistillate flowers on a given individual. In this case, the individual
plants are unisexual with regard to expression and, as a result, populations of
dioecious taxa include both 'male' and 'female' individuals.
FRUITS
Fleshy Fruits
Berry
- fruit with the pericarp fleshy throughout and seeds inside the fruit; EX:
Tomato
Pome
- fleshy fruit produced by an inferior ovary; the endocarp enclosing many seeds,
commonly called the core; EX: Apple
Stone
(or) Drupe - a fleshy fruit, usually one seeded; the seed is enclosed in a
stony endocarp; EX: Cherry
Specialized Berries
Hesperidium
- a berry with leathery exocarp and mesocarp; the endocarp is segmented and very
juicy; EX: Orange
Pepo
- a berry with a hard and very thick exocarp or rind; EX: Cantaloupe
Dry Indehiscent Fruits - dry fruits
which do not split along definite lines to release seeds at maturity
Acorn
- single celled, single seeded fruit of oaks
Samaras
- a dry, non-dehiscent, winged fruit
Caryopsis
or Grain--one seed which has the seedcoat fused to the pericarp
Nut--one
seeded by abortion (only one ovule matures), usually hard-shelled
Dry Dehiscent Fruits - dry fruits
which split along definite lines to release seeds at maturity
Legume
- single celled, splits along two sutures releasing the seeds
Silique
- consists of two cells, splits along two sutures releasing the seeds
Capsule
- short and rounded fruit, consists of more than one carpel
Follicle- from
one simple pistil, dehisces along one suture
Schizocarp- from
a compound pistil, splits into mericarps (pieces) which enclose one or more
seeds and resemble fruits themselves.
OTHER TYPES OF FRUITS
Aggregate- fruit
composed of mature ovaries from separate pistils of ONE flower. Can be an
aggregate of achenes, drupelets,
samaras, etc.
Multiple- fruit
composed of mature ovaries from separate pistils from SEVERAL flowers. Can be a
multiple of follicles, drupelets, etc. A pineapple is a multiple of berries
Accessory- fruit
where the "fruit" part is derived from something other than ovary
tissue. E.g., a strawberry is a swollen receptacle; the "seeds" on the
surface are the true fruits, achenes. Some put hips and pomes in this category.
![]()