MUSCLE TISSUE:
Muscle tissue contains very long cells which are highly specialized to shorten. This action produces movement in some body part.
There are three types of muscle tissue: Skeletal, smooth, and cardiac.
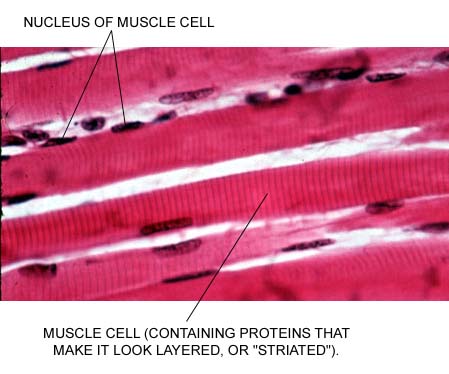
Skeletal muscle is striated (striped or layered in appearance) and is under voluntary control. This type of tissue will cause the movement of external body parts. Skeletal muscle works primarily with osseous (connective) tissue. When you have a "steak" for dinner, it is usually a skeletal muscle. Notice the striated appearance of the tissue and the elongated cells in this picture:

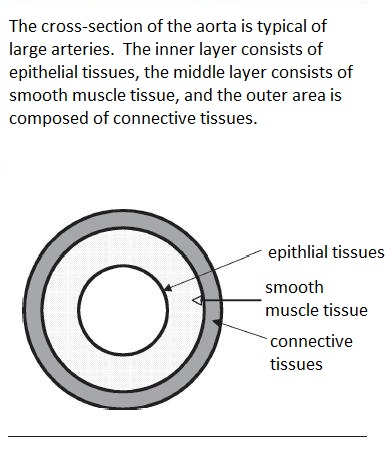
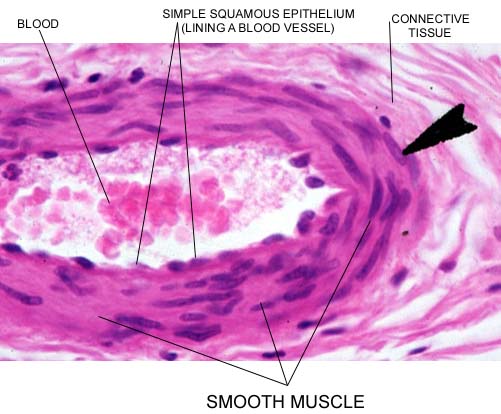
Smooth muscle is so named because of its smooth appearance. This tissue is under involuntary control, and is usually found in walls of hollow organs, such as arteries. It typically constricts or dilates the lumen (space) of a hollow organ. Notice the lumen in the following image. It is formed by epithelial tissue, but the adjacent layer is smooth muscle, which functions primarily to constrict or dilate the lumen:
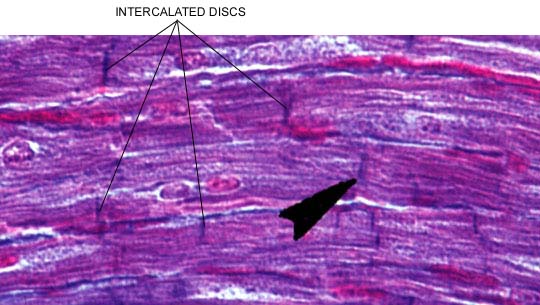
Cardiac muscle is striated in appearance and is under involuntary control. This type of tissue is only found in the heart, and its contractions force blood out of that organ. Cardiac muscle can be distinguished from skeletal muscle because of its branching cells and intercalated discs, which are located at the junctions of cell branches. Notice the striated appearance of the tissue and the intercalated discs in this picture: